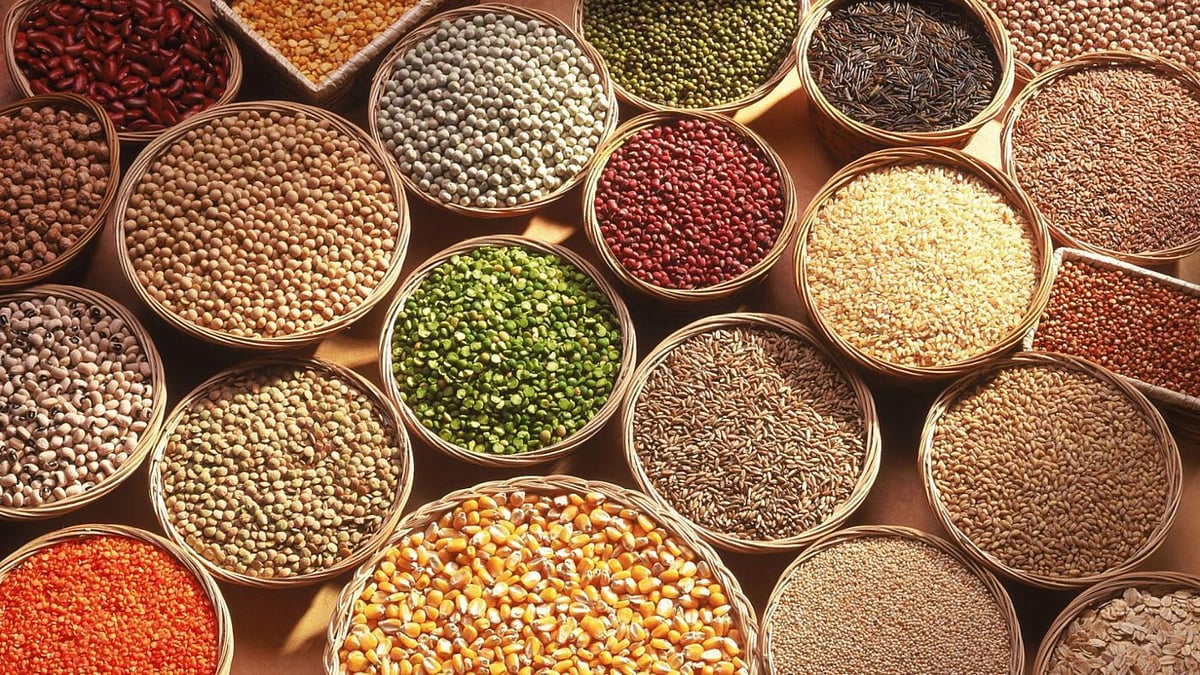
Hyderabad: A new study has shown that eating millets reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and helps manage blood glucose levels in people with diabetes. The study indicates the potential to design appropriate meals with millets for diabetic and pre-diabetic people as well as for non-diabetic people as a preventive approach.
Drawing on research from 11 countries, the study published in Frontiers in Nutrition shows that diabetic people who consumed millets as part of their daily diet saw their blood glucose levels drop 12-15% (fasting and post-meal), and blood glucose levels went from diabetic to pre-diabetes levels.
The HbA1c (blood glucose bound to hemoglobin) levels lowered on average 17% for pre-diabetic individuals, and the levels went from prediabetic to normal status. These findings affirm that eating millets can lead to a better glycemic response.
The authors reviewed 80 published studies of which 65 were eligible for a meta-analysis involving about 1,000 human subjects, making this analysis the largest systematic review on the topic till date, said International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT).
“No one knew there were so many scientific studies undertaken on millets’ effect on diabetes. These benefits were often contested, and this systematic review of the studies published in scientific journals has proven that millets keep blood glucose levels in check, reducing the risk of diabetes, and has shown just how well these smart foods do it,” said Dr. S Anitha, the study's lead author and a senior nutrition scientist at International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT).
“Diabetes contributed to very high disease burden from 1990-2016 in India. Diabetes-related health expenditure was over $7 million. There is no easy solution, and it requires a lifestyle change, and diet is a very important part of this. This study provides one part of the solution useful for individuals and governments. How we use this and implement it into programs needs careful planning,” said Hemalatha, Director, National Institute of Nutrition (NIN).
Raj Bhandari, one of the study’s authors and a representative on the Indian National Technical Board of Nutrition, noted that additional attention to our health has been accelerated due to Covid-19 and diabetics are even more vulnerable to the virus. “Our diets play a critical role and if we could bring millets back as a major part of our diet, we would not only help in controlling diabetes, but we would also be adding important nutrients to our plate.”