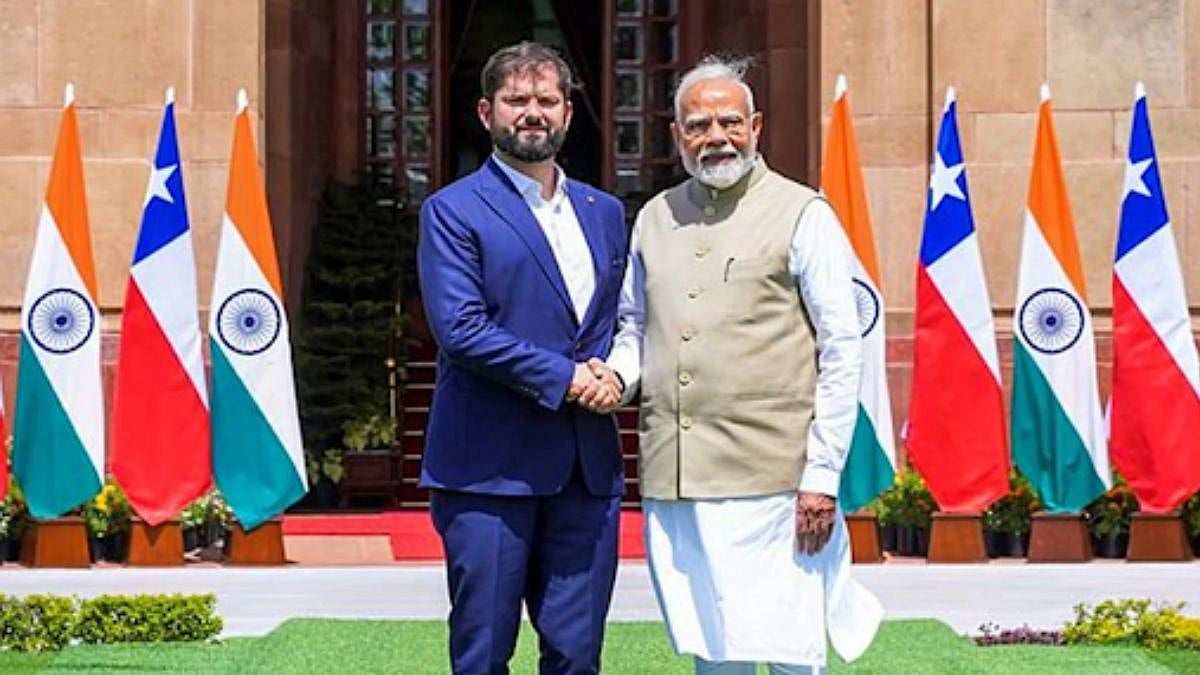
New Delhi, Nov 16: The next round of negotiations between India and Chile on the proposed free trade agreement is expected to be held in December here, an official said. The pact with the the South American nation may help India access critical minerals, which are key inputs for electronics, auto, and solar sectors.
Third Round of CEPA Talks Concluded in Santiago
India and Chile concluded the third round of negotiations for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) in Santiago. The four-day talks concluded on October 30. India is seeking preferential treatment for critical minerals in Chile under the pact.
Strategic Focus on Latin American Partnerships
India's growing trade engagement with Chile reflects its strategic focus on building stronger partnerships with the Latin American region through mutually beneficial and comprehensive economic cooperation frameworks, the official said.
India and Chile implemented a preferential trade agreement (PTA) in 2006 and are now negotiating to widen its scope for a comprehensive economic partnership agreement.
CEPA to Broaden Trade Scope Across Sectors
CEPA aims to build upon the existing PTA between the two nations and seeks to encompass a broader range of sectors, including digital services, investment promotion and cooperation, MSMEs (micro, small and medium enterprises), and critical minerals.
Bilateral Trade Trends Between India and Chile
The bilateral trade between India and Chile is modest. In 2024-25, India's exports to Chile were down 2.46 per cent to just USD 1.15 billion. Imports, however, grew 72 per cent to USD 2.60 billion.
The largest Indian exports to Chile are auto and pharma. The biggest imports from Chile are minerals worth around USD 1.58 billion. Other products imported from Chile are copper and chemicals.
Chile is the fifth-largest trading partner of India in the LAC (Latin American countries) region.
Also Watch:
India’s Export Basket to Chile
India's exports to Chile are diversified and constitute motor vehicles/cars, drug formulations, chemicals, iron and steel products, man-made yarn, fabrics, cotton fabrics, made-ups, RMG (ready-made garments), auto components, electric machinery and equipment, leather goods, rubber products, aluminium and its products, and ceramics.
(Disclaimer: Except for the headline, this article has not been edited by FPJ's editorial team and is auto-generated from an agency feed.)